What Are Backconnect Proxies
Backconnect proxies, also known as rotating proxies or reverse proxies, are a type of proxy server that automatically rotates IP addresses from a pool of proxies each time a connection request is made. Unlike traditional proxies, where a single IP address is assigned to a user for the duration of their session, backconnect proxies dynamically assign a different IP address for each connection or request.
We provide real residential and mobile proxies from real commercial Internet service providers with IPs that work with any proxy app and on any website.
Our mobile network has four rotation setups:
1) 5min auto IP rotations (only for Premium orders) – your proxy will rotate into a new IP at every 5 minutes.
2) 10min auto IP rotations ( only for Premium orders) – your proxy will rotate into a new IP at every 10 minutes.
3) 30min auto IP rotations (for both Premium and Standard orders) – your proxy will rotate into a new IP at every 30 minutes.
4) Extended rotations (for both Premium and Standard orders) – you’ll be allocated IPs with extended rotation periods that can last for up to 6 hours.
The residential network has two options:
1) Request-based rotation – your IP will rotate on each request of your tool or browser (such as page refresh)
2) Sticky IP sessions – you’ll get a sticky IP that can be used from a few minutes up to one hour, which you can change on demand sooner than its expiration time.
If you need help placing an order please click here: https://hydraproxy.com/how-to-order/
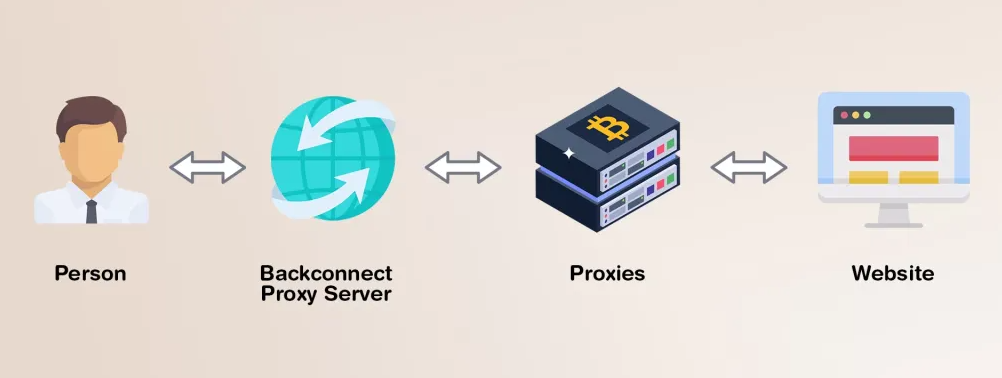
How Do Backconnect Proxies Work?
Backconnect proxies work by dynamically assigning users different IP addresses from a pool of proxies each time they establish a connection or make a request. This rotation of IP addresses helps to enhance anonymity, distribute load, and circumvent IP-based restrictions. Here’s a more detailed explanation of how backconnect proxies work:
- Connection to Proxy Service: Users connect to a backconnect proxy service, typically through a client application or by configuring their network settings to route traffic through the proxy service.
- Assignment of Proxy IP: When a connection request is made to the backconnect proxy service, the service assigns the user a proxy IP address from its pool of available proxies. This initial assignment may be random or based on factors such as server load or geographic location.
- Request Routing: The user’s connection request is forwarded to the proxy server associated with the assigned IP address. The proxy server acts as an intermediary between the user and the destination server, forwarding requests and responses back and forth.
- Rotation of IP Addresses: After a certain period or after a specified number of requests, the backconnect proxy service rotates the user’s assigned IP address. This rotation may occur automatically according to predefined rotation intervals or based on user settings.
- Load Balancing and Redundancy: Backconnect proxy services often employ load balancing techniques to distribute connection requests across multiple proxy servers. This helps to prevent overloading any single proxy server and ensures better performance and reliability. Additionally, redundancy measures may be in place to handle server failures or downtime.
- Anonymity and Security: By rotating IP addresses, backconnect proxies enhance user anonymity since their internet traffic appears to originate from different IP addresses each time they make a connection. This makes it more difficult for websites and online services to track or identify users based on their IP address. Furthermore, the use of proxies can provide an additional layer of security by masking the user’s actual IP address from potential threats or malicious actors.
- Proxy Management: Backconnect proxy services handle the management of proxy servers, including maintaining and updating the pool of available proxies, handling rotation logic, monitoring proxy performance, and addressing any issues that may arise.
Pros and Cons of Backconnect Proxies
Backconnect proxies offer several advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific use case and requirements of the user. Here are some of the pros and cons of using backconnect proxies:
Pros:
- Anonymity: Backconnect proxies rotate IP addresses, enhancing user anonymity by making it difficult for websites and online services to track or identify users based on their IP address. This can be beneficial for privacy-sensitive activities.
- IP Rotation: Backconnect proxies automatically rotate IP addresses from a pool of proxies, reducing the risk of IP-based blocking or detection. This rotation helps to maintain access to websites and online services without being flagged for suspicious behavior.
- Bypassing Restrictions: Backconnect proxies can help bypass IP-based restrictions imposed by websites or online services. By using different IP addresses for each connection, users can circumvent bans, blocks, or access restrictions based on IP addresses.
- Load Balancing: Backconnect proxy services often employ load balancing techniques to distribute connection requests across multiple proxy servers. This helps to prevent overloading any single server and ensures better performance and reliability.
- Scalability: Backconnect proxy services can easily scale to accommodate changing traffic patterns and user requirements. Users can dynamically adjust the number of proxies they use and scale up or down as needed.
Cons:
- Cost: Backconnect proxy services may incur additional costs compared to traditional proxies due to the dynamic IP rotation and load balancing features. Users may need to pay subscription fees or usage-based charges for access to the service.
- Performance Overhead: The use of backconnect proxies can introduce additional latency and overhead compared to direct connections, especially if the proxy service experiences high demand or network congestion.
- Reliability: Reliability can be a concern with backconnect proxies, as users rely on the proxy service to manage a pool of proxies, handle rotation logic, and ensure uptime. Issues such as proxy server failures or downtime can disrupt service availability.
- Detection Risks: While backconnect proxies can help evade IP-based blocking or detection to some extent, they are not foolproof. Websites and online services may employ sophisticated detection techniques to identify and block proxy traffic, potentially leading to access issues or bans.
- Security Risks: Using backconnect proxies introduces additional security risks, as users’ internet traffic passes through intermediary servers controlled by the proxy service. Users must trust the proxy service provider to handle their data securely and responsibly.
What Are Backconnect Proxies Used For?
Backconnect proxies are used for various purposes that benefit from features such as IP rotation, anonymity, and bypassing restrictions. Some common use cases for backconnect proxies include:
- Web Scraping and Data Mining: Backconnect proxies are widely used for web scraping and data mining tasks where users need to collect data from multiple sources on the internet. The ability to rotate IP addresses helps to avoid getting blocked by websites and to gather data anonymously.
- SEO Monitoring and Research: SEO professionals use backconnect proxies to monitor search engine rankings, analyze competitor websites, and gather data for keyword research. By rotating IP addresses, they can gather accurate and unbiased data without triggering rate limits or IP bans.
- Ad Verification and Market Research: Backconnect proxies are used for ad verification to ensure that advertisements are being displayed correctly and to monitor competitors’ advertising strategies. They are also used for market research to gather data on pricing, product availability, and customer reviews from various websites.
- Social Media Management: Social media managers use backconnect proxies to manage multiple social media accounts and automate tasks such as posting content, engaging with followers, and monitoring trends. The anonymity provided by backconnect proxies helps to avoid detection and account restrictions.
- Web Security and Penetration Testing: Security professionals use backconnect proxies for penetration testing and security assessments of websites and web applications. By simulating attacks from multiple IP addresses, they can identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the target system’s defenses.
- Anonymous Browsing and Privacy Protection: Individuals use backconnect proxies to browse the internet anonymously and protect their privacy online. By masking their IP address and location, they can prevent websites and online services from tracking their online activities.
- E-commerce and Price Monitoring: E-commerce businesses use backconnect proxies to monitor competitor prices, track product availability, and gather market intelligence. By rotating IP addresses, they can gather data without being detected or blocked by competitors’ websites.
- Content Distribution and Load Testing: Backconnect proxies are used for content distribution and load testing to simulate traffic from multiple geographic locations and test the performance and scalability of web servers and applications.
Any difference between Rotating Proxies and Backconnect Proxies?
“Rotating proxies” and “backconnect proxies” are often used interchangeably, but there can be subtle differences in how these terms are interpreted depending on the context and the specific features offered by proxy providers. In general, both rotating proxies and backconnect proxies refer to proxies that automatically rotate IP addresses from a pool of proxies. However, there may be variations in their implementation and functionality:
- Rotating Proxies:
- Rotating proxies typically refer to proxies that rotate IP addresses at regular intervals or after a certain number of requests. This rotation can occur based on predefined time intervals (e.g., every 5 minutes) or request thresholds (e.g., every 100 requests).
- Rotating proxies may rotate IP addresses sequentially, cycling through the pool of available proxies in a predefined order, or randomly, selecting IP addresses from the pool in a non-sequential manner.
- Rotating proxies are commonly used for tasks such as web scraping, data mining, and market research, where frequent IP rotation helps to evade detection, bypass IP-based restrictions, and prevent blocking.
- Backconnect Proxies:
- Backconnect proxies are a type of rotating proxy that offers additional features such as load balancing, redundancy, and automatic failover.
- Backconnect proxies typically operate by routing connections through a gateway server that dynamically assigns users different IP addresses from a pool of proxies. Each time a connection is made, the user is assigned a different IP address from the pool.
- Backconnect proxies may employ load balancing techniques to distribute connection requests across multiple proxy servers, ensuring better performance and reliability.
- Backconnect proxies are commonly used for applications requiring frequent IP rotation, anonymity, and bypassing IP-based restrictions, such as web scraping, ad verification, and data aggregation.
In summary, while both rotating proxies and backconnect proxies involve the automatic rotation of IP addresses, backconnect proxies often provide additional features such as load balancing and redundancy. The terminology used to describe these proxies may vary among proxy providers, so it’s essential to carefully review the features and functionality offered by each service to determine the best fit for specific use cases.