What are Residential Proxies ?
When people talk about proxies being “blocked” or “detected,” they’re often really talking about the source of the IP address. This is where residential proxies enter the conversation, and why they’re treated differently from many other proxy types.
A residential proxy routes traffic through IP addresses that belong to real household internet connections. To websites, these requests look like they’re coming from everyday users browsing from their homes. Because of this, residential traffic tends to blend in naturally, especially on platforms that aggressively filter automated or repetitive behavior.
This is very different from proxies that rely on data center infrastructure. Data center IPs are fast and affordable, but they’re also easier for websites to recognize. Large blocks of traffic coming from servers instead of consumer networks often trigger defenses, even when the activity itself is legitimate.
Residential proxy networks reduce that friction. They’re commonly used for tasks that require authenticity, such as viewing localized search results, verifying ads as real users would see them, or collecting public data from sites that limit automated access. Because the IPs are tied to real locations, targeting by city or country is also more accurate.
That said, residential proxies are not magic. Quality matters a lot. Overused or poorly managed IPs can still be flagged, which is why serious providers invest heavily in sourcing, rotation logic, and reputation management. The goal is to maintain natural traffic patterns, not overwhelm sites with requests.
This is also why residential proxies are usually part of paid services rather than free tools. Maintaining a clean residential network requires ongoing effort, monitoring, and compliance with usage standards.
HydraProxy treats residential IPs as a precision tool rather than a mass solution. By focusing on stability and controlled access, it aims to provide the benefits of residential traffic without the unpredictability that frustrates many users when they first explore this option.
For anyone who needs proxy traffic to behave like a real person behind a screen, residential proxies are often the closest match.
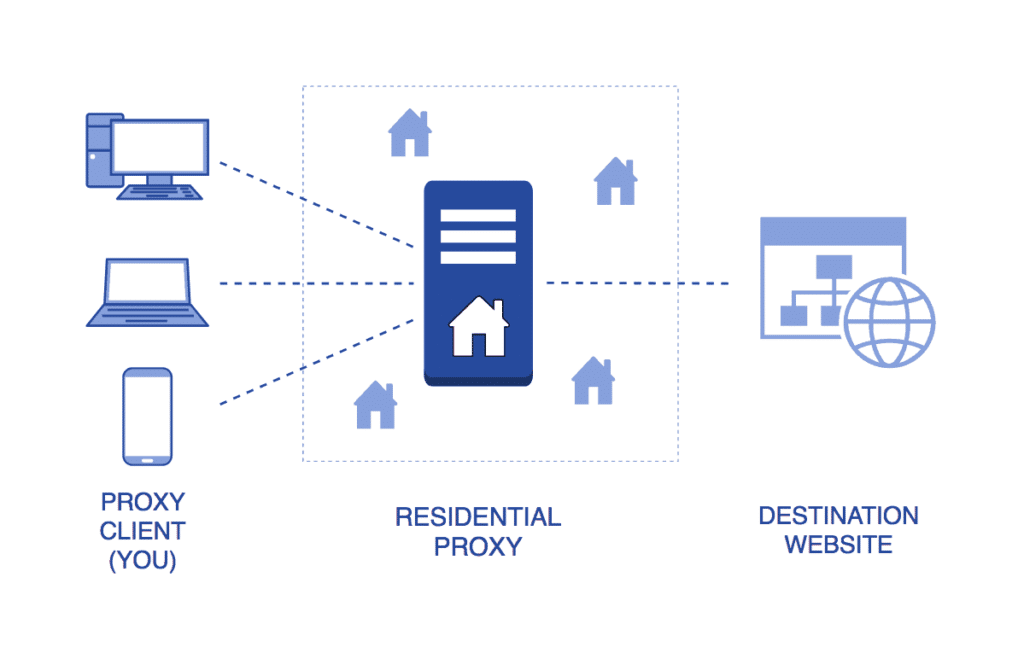
Here’s how residential proxies work:
Residential IPs originate from real consumer internet connections. Unlike datacenter IPs, which are owned by hosting providers, residential IPs are registered to ISPs and allocated to individual households.
1. Acquisition of Residential IP Addresses:
In practice, residential proxy networks source IPs through:
- User-opted devices connected to home networks
- ISP-assigned address pools
- Peer-based or managed proxy infrastructures
Because these IPs belong to legitimate consumer networks, they tend to carry a higher level of trust with many websites.
2. Proxy Server Infrastructure:
Residential proxy providers set up proxy servers that act as intermediaries between the user’s device and the internet. These proxy servers are configured to route user requests through the residential IP addresses in their pool.
3. Request Routing:
When a user sends a request through a residential proxy, the proxy server selects an available residential IP address from its pool and routes the request through that IP address. This makes it appear as though the request is originating from a genuine residential user.
4. IP Rotation:
To maintain anonymity and avoid detection, residential proxy networks often employ IP rotation. This means that the proxy server periodically changes the IP address used for outgoing requests, cycling through different residential IP addresses in its pool.
Our residential network has two options:
a) Request-based rotation – your IP will rotate on each request of your tool or browser (such as page refresh)
b) Sticky IP sessions – you’ll get a sticky IP that can be used from a few minutes up to one hour, which *you can change on demand* sooner than its expiration time.
If you need more details regarding our residential proxies click here.
Also if you need help placing an order for residential proxies please click here: https://hydraproxy.com/how-to-order/
5. Response Forwarding: After receiving the requested data from the destination server, the residential proxy server forwards the response back to the user’s device. From the perspective of the destination server, the request appears to originate from the residential IP address assigned by the ISP.
There are several reasons why individuals and businesses use residential proxies:
1. Anonymity and Privacy:
Residential proxy networks offer a higher level of anonymity compared to datacenter proxies because they route internet traffic through genuine residential IP addresses. This makes it more difficult for websites and online services to identify and track the user’s real IP address, enhancing privacy and anonymity online.
2. Bypassing Restrictions:
Residential proxy networks allow users to bypass geo-restrictions and access content that may be limited to specific regions or countries. By routing internet traffic through residential IP addresses from different locations, users can access region-restricted websites, streaming services, and online content.
3. Web Scraping and Data Collection:
Residential proxy networks are commonly used for web scraping and data collection tasks. By rotating through a pool of residential IP addresses, users can scrape data from websites without getting blocked or flagged. Residential proxies mimic genuine user behavior, making it more challenging for websites to detect and block automated scraping activities.
4. Ad Verification and Market Research:
Advertisers and marketers use residential proxy networks to verify the placement and visibility of online advertisements. By accessing websites through residential IP addresses, they can ensure that ads are displayed correctly and reach the intended audience. Residential proxies also facilitate market research by providing access to localized content and user demographics.
5. Social Media Management:
Residential proxy networks are often used in social media management to automate tasks such as account creation, posting, and engagement. By rotating through residential IP addresses, users can avoid detection by social media platforms and prevent their accounts from being flagged or suspended for suspicious activity.
6. E-commerce and Sneaker Bots:
In the e-commerce industry, residential proxy networks are used by individuals and businesses to automate tasks such as purchasing limited-edition sneakers, tickets, or other high-demand products. By rotating through residential IP addresses, users can bypass purchase limits, avoid IP bans, and increase their chances of successfully completing transactions.
Overall, residential proxy networks provide users with a range of benefits, including anonymity, bypassing restrictions, facilitating web scraping and data collection, verifying online advertisements, and automating various online tasks. However, it’s essential to use residential proxies responsibly and in compliance with the terms of service of the websites and services being accessed.
Rotating vs Static Residential Proxies
Residential proxies are commonly offered in two forms: rotating and static.
Rotating Residential Proxies
With rotating residential proxies, the IP address changes automatically at regular intervals or after a certain number of requests. Rotation helps distribute traffic across multiple IPs and reduces repeated requests from a single address.
This approach is often used for:
- Web data collection
- Price monitoring
- Market research
- Accessing rate-limited content
Static Residential Proxies
Static residential proxies provide a residential IP address that remains consistent over time. Although the IP still belongs to a residential ISP, it does not rotate frequently.
Static residential proxies are typically preferred when:
- Session stability is required
- Long-term logins are needed
- A consistent IP identity matters
The choice between rotating and static residential proxies depends on whether consistency or distribution is more important for the task.
Residential Proxy vs Datacenter Proxy
The main difference between residential and datacenter proxies lies in how their IPs are perceived by websites.
- Residential proxies use IPs associated with real households and ISPs
- Datacenter proxies use IPs from cloud or hosting providers
Datacenter proxies often offer higher speeds and lower costs, but they are also easier for websites to identify and block. Residential proxies trade some performance for increased legitimacy and lower detection risk.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Using residential proxies raises questions about legality and ethics, especially regarding how IP addresses are sourced and used.
Key considerations include:
- Whether IP owners have given informed consent
- Compliance with local laws and regulations
- Respecting website terms of service
- Avoiding misuse, fraud, or unauthorized access
While residential proxies themselves are not illegal, improper use or lack of transparency can create legal or ethical issues. Responsible usage is essential.
Summary
Residential proxy networks reduce that friction. They’re commonly used for tasks that require authenticity, such as viewing localized search results, verifying ads as real users would see them, or collecting public data from sites that limit automated access. Because the IPs are tied to real locations, targeting by city or country is also more accurate.
That said, residential proxies are not magic. Quality matters a lot. Overused or poorly managed IPs can still be flagged, which is why serious providers invest heavily in sourcing, rotation logic, and reputation management. The goal is to maintain natural traffic patterns, not overwhelm sites with requests.
This is also why residential proxies are usually part of paid services rather than free tools. Maintaining a clean residential network requires ongoing effort, monitoring, and compliance with usage standards.
HydraProxy treats residential IPs as a precision tool rather than a mass solution. By focusing on stability and controlled access, it aims to provide the benefits of residential traffic without the unpredictability that frustrates many users when they first explore this option.
For anyone who needs proxy traffic to behave like a real person behind a screen, residential proxies are often the closest match.
Understanding how residential IPs are sourced, how rotation works, and when residential proxies are appropriate helps ensure they are used effectively and responsibly.